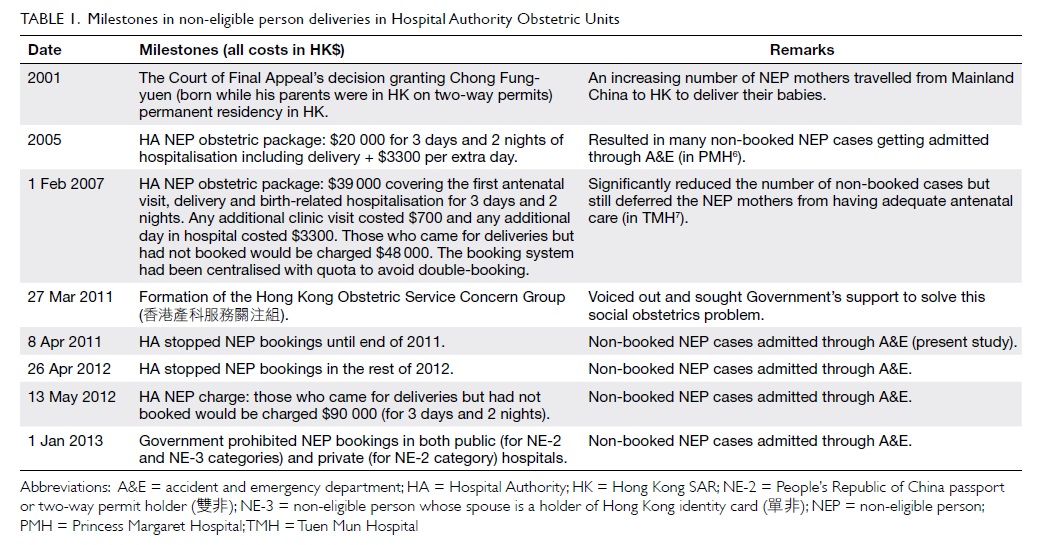
Double free flaps for reconstruction of complex/composite defects in head and neck surgery
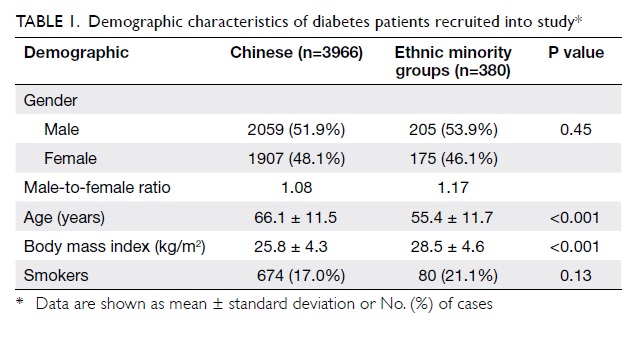
Hong Kong Med J 2014 Aug;20(4):279–84 | Epub 28 Mar 2014
DOI: 10.12809/hkmj134113
© Hong Kong Academy of Medicine. CC BY-NC-ND 4.0
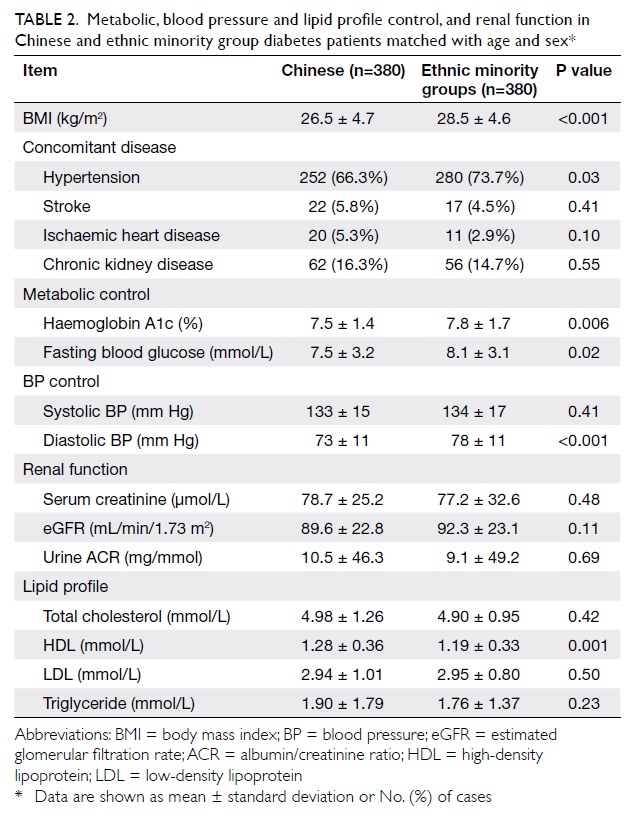
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Double free flaps for reconstruction of complex/composite defects in head and neck surgery
Kevin WL Mo, MRCS1;
Alexander Vlantis, FCS(SA)ORL2;
Eddy WY Wong, FRCSEd(ORL), FHKCORL2;
TW Chiu, FHKAM (Surgery)1
1 Division of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery, Department of Surgery, Prince of Wales Hospital, Shatin, Hong Kong
2 Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, Prince of Wales Hospital, Shatin, Hong Kong
Corresponding author: Dr TW Chiu (torchiu@surgery.cuhk.edu.hk)
Abstract
Objective: To demonstrate the feasibility of double free
flap surgery in head and neck reconstruction.
Design: Descriptive case series.
Setting: A university-affiliated hospital in Hong
Kong.
Patients: Twelve patients with head and neck cancer
(encountered over a 2.5-year period) who had
reconstructive surgery with planned simultaneous
double free flaps.
Results: The mean total operating time was 660 minutes
and there were no flap failures. Postoperative stays
ranged from 11 to 82 days; nine patients were
discharged within 3 weeks and seven were able to
maintain their weight with oral feeding. The survival
rate up to 1 year was 64%.
Conclusion: The use of double free flaps is an option
worth considering for complex head and neck
defects in carefully selected patients.
New knowledge added by this
study
- Double free flaps can be used with good flap success rates, operating times, and patient outcomes.
- Concerns over the use of double free flaps in head and neck reconstruction should not deter experienced microsurgeons from this procedure whenever they are deemed to offer significant advantages, in terms of reconstructions involving large bulks, multiple surfaces, or multiple tissue types.
Introduction
The use of microvascular free flaps for the
reconstruction of defects following the resection
of head and neck cancer is a complex but routine
procedure. However, single flaps may not be
sufficient for some defects that are either too large or
warrant composite tissues. In particular, resection of
advanced tumours of the oral cavity results in complex
oromandibular defects that often involve bone, oral
lining, external skin, and soft tissue. The free fibular
osteocutaneous (FO) flap is well established as a
workhorse flap for mandible reconstruction,1 which
provides 25 to 30 cm of straight bone of good quality
that can be contoured, as well as a skin paddle for
soft tissue coverage when needed. The pedicle has
an acceptable length and its vessels have a good
diameter. It is therefore our preferred option for
restoring mandibular defects and for lining the oral
cavity.
However, the size of the skin paddle is limited1
and may not be supplied by the same vessel as the
bone.2 Thus, with larger composite defects, a single fibula flap cannot provide sufficient soft tissue
coverage and a second skin flap may be necessary.
Some surgeons nevertheless elect to avoid a
second free flap by choosing either a pedicled flap
or alloplastic material. We therefore set out to
demonstrate the feasibility of resorting to double free
flap surgery in head and neck reconstruction.
Our choice for additional soft tissue is the
anterolateral thigh (ALT) flap that provides up to
630 cm2 of skin.3 On occasions when the vascularity
of the fibula flap skin paddle is deemed borderline,
the ALT can be harvested with multiple skin islands
so as to cover both the inner lining and the external
skin. Harvest of the FO and ALT flaps can proceed at
the same time as tumour excision, without the need
for patient re-positioning, which is an important
logistical advantage. Like most surgeons, whenever
possible we prefer using separate anastomoses for
double flaps rather than sequential linking or ‘flow
through’,4 5 6 as some studies5 6 suggest that the latter
has more complications (possibly due to increased
thrombogenicity or a ‘steal’ phenomena).
Methods
We conducted a retrospective case review of patients
in our institution with head and neck cancer who had
reconstruction with planned simultaneous double
free flaps over a 2.5-year period (from November
2010 to August 2013). For all cases we deployed two
surgical teams; reconstructions were performed
(one surgeon) at the same time as tumour excision
(other surgeons). Preoperatively, handheld Doppler
probes were used to locate the skin perforators for
both flaps. The peroneal artery was sacrificed in the
harvest of fibula flaps and adequacy of the remaining
vessels was screened by palpation of the dorsalis
pedis and posterior tibial pulses. An angiogram was
used in only one patient with a history of peripheral
vascular disease.
The FO flap was harvested first using a lateral
approach; a sterile tourniquet was placed on the upper
thigh but not inflated. A skin island was harvested in
nine out of 10 fibula flaps. In one patient, the skin
island was not perfused by the peroneal artery and
thus not harvested. In another, the vascularity of the
skin island was deemed suboptimal and therefore
not used. The fibula flap was kept in situ after
isolation of its vascular pedicle while the ALT was
harvested. Intramuscular perforators to the thigh
skin island were skeletonised in all cases so as to
completely visualise the vessels. Once the surgical
margins were deemed clear by frozen sections, the
final dimensions of the ALT flaps were determined
when the final defect was defined.
Whenever possible, intermaxillary fixation was
used to hold the mandible and maxilla in an optimal
position, and ‘by eye’ the fibula was osteotomised to
fit (average 1-2 osteotomies). Two sets of mini-plates
were used per osteotomy site so as to maximise
rotational stability. The use of 2.5 x or 3.5 x loupes by the reconstructive surgeon allowed micro-anastomoses
of the vessels, whilst insetting of the
flap was completed.
Illustrative case
A 58-year-old man was referred to our centre with
a second recurrence of a squamous cell carcinoma
of his tongue. Three years earlier, he had had a
partial right glossectomy with a selective neck
dissection for a pT2N0 lesion. One year later he
underwent a complete neck dissection for a
right nodal recurrence, and another year later he
had had a reconstruction with a pectoralis major
myocutaneous flap (PMMF) after total glossectomy
for local tumour recurrence. After the tumour was
resected, he had a bony defect from one angle of the
mandible to the other, and a soft tissue defect that
involved the entire inferior oral cavity down to the
chin and anterior neck skin, which left a 3-cm rim of
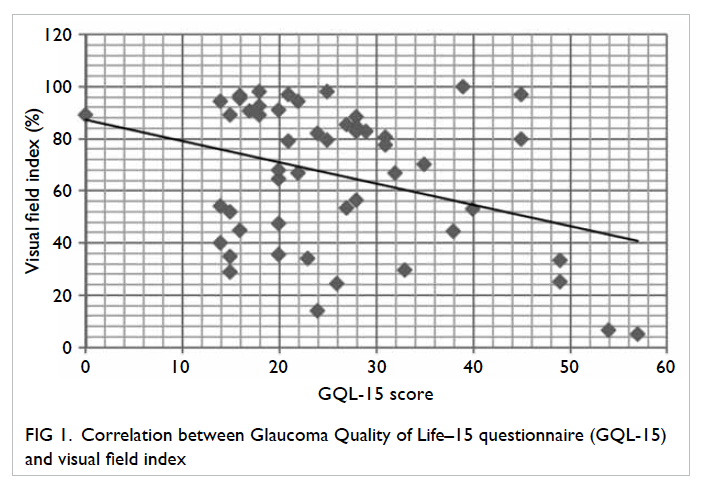
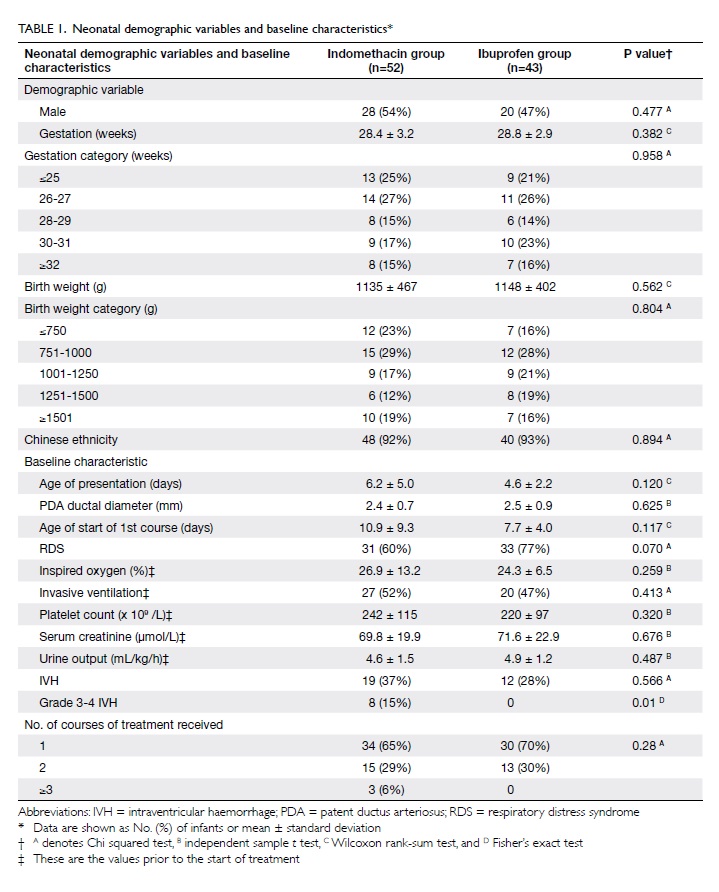
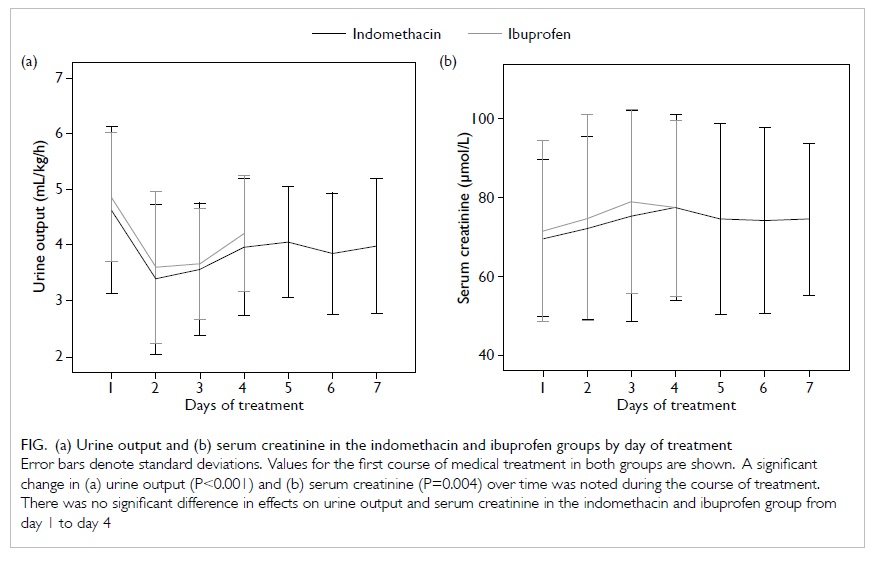
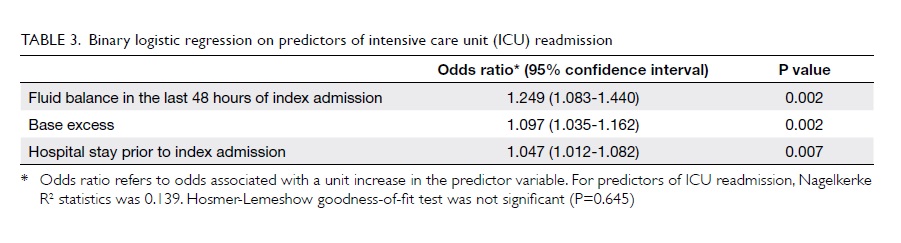
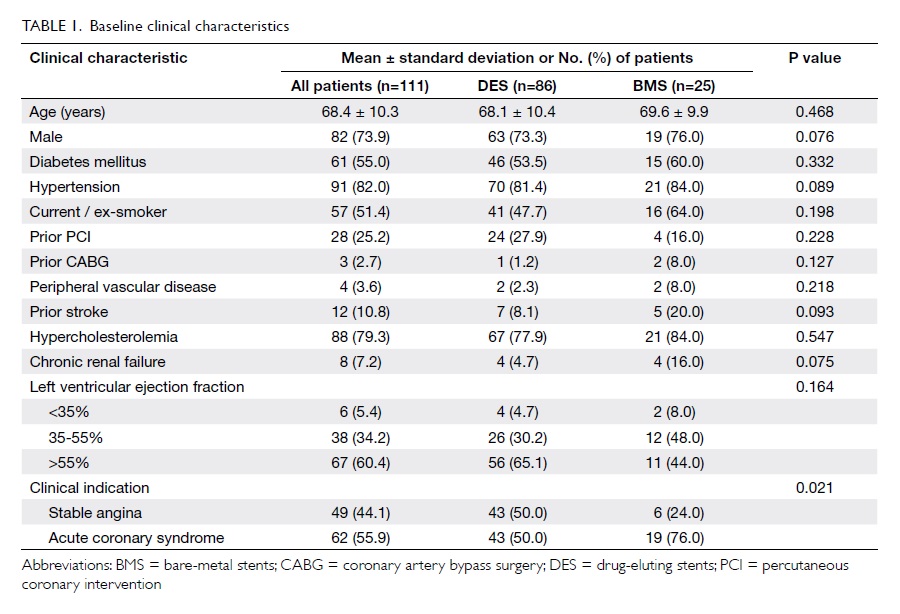
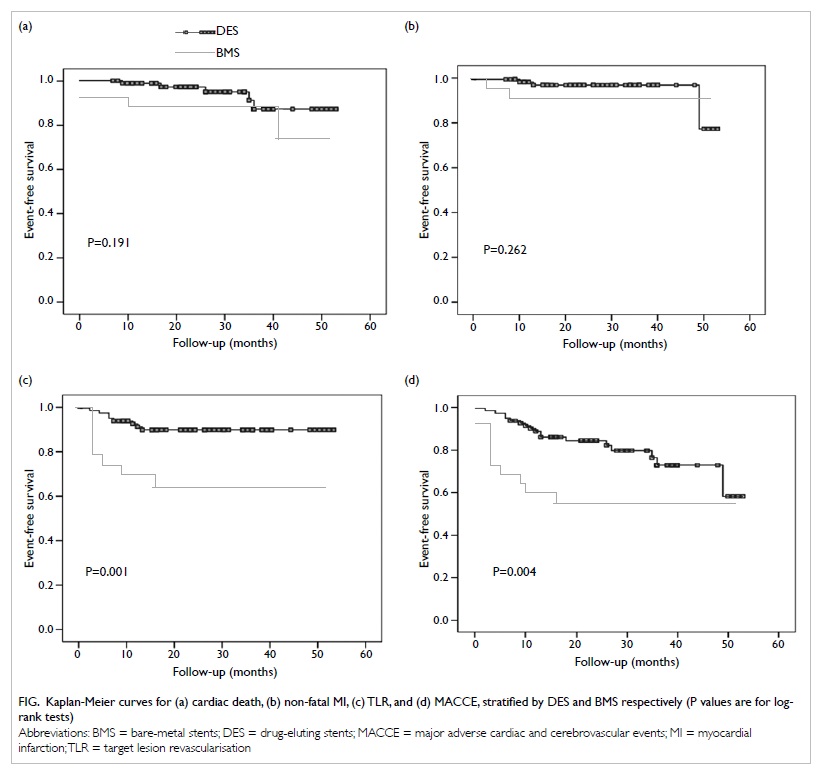
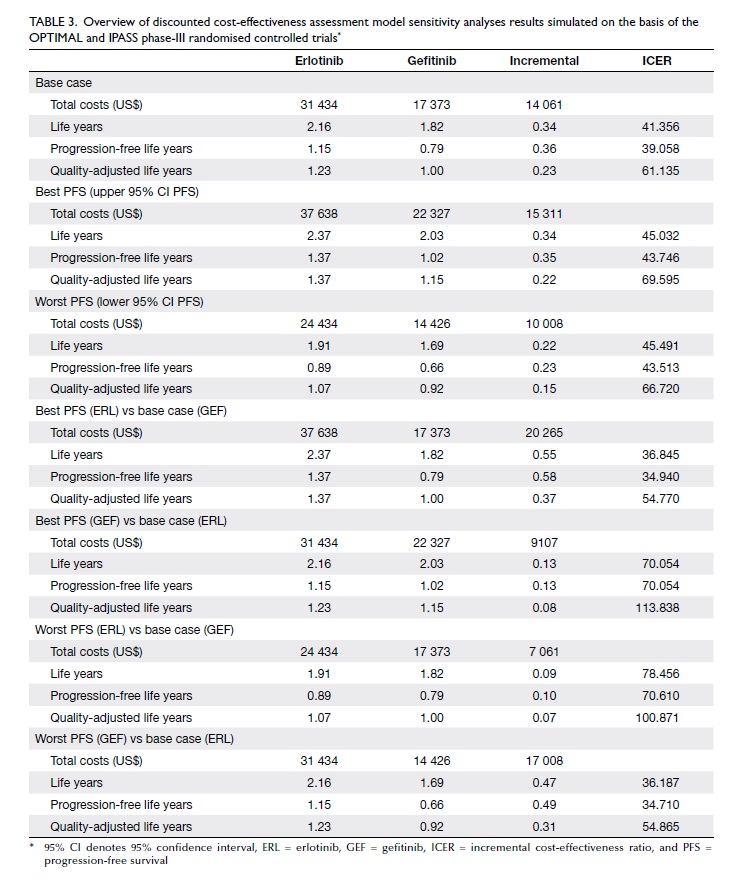
lower lip (Fig 1).
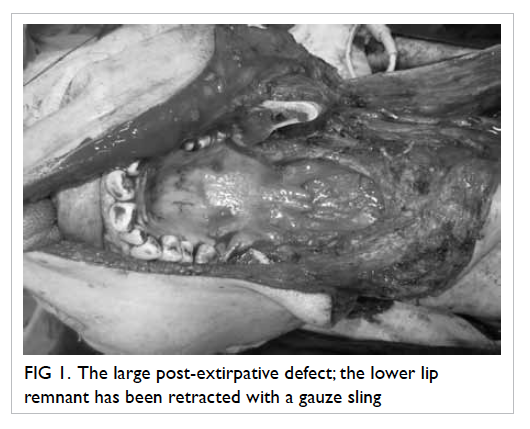
Figure 1. The large post-extirpative defect; the lower lip remnant has been retracted with a gauze sling
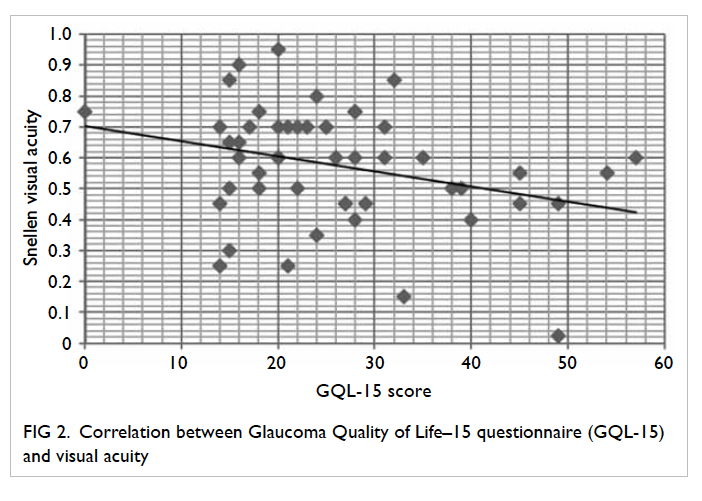
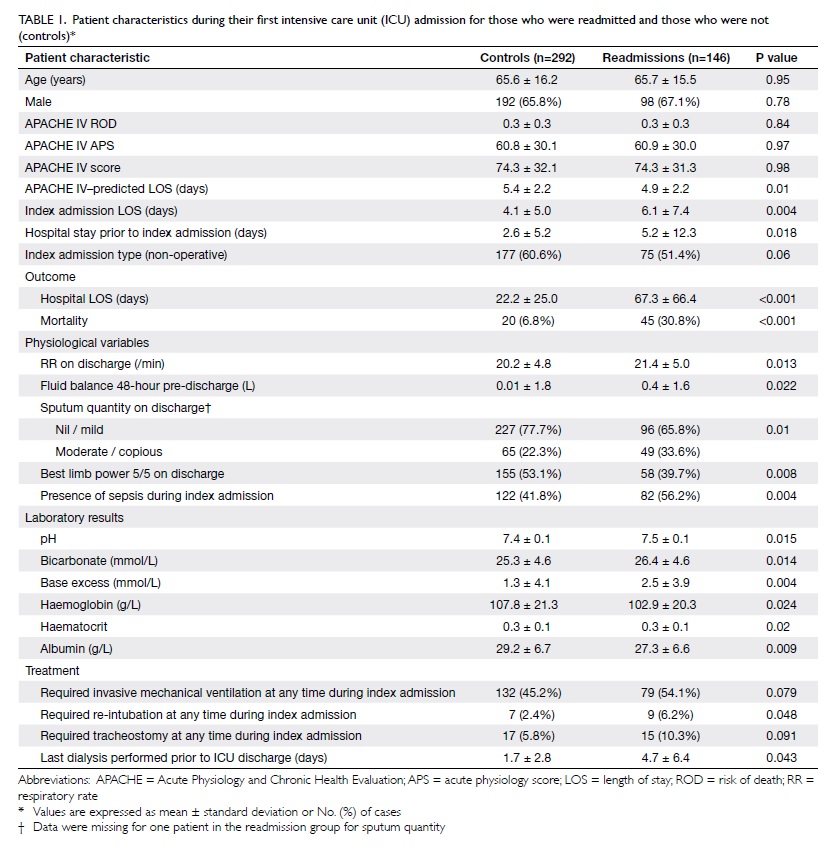
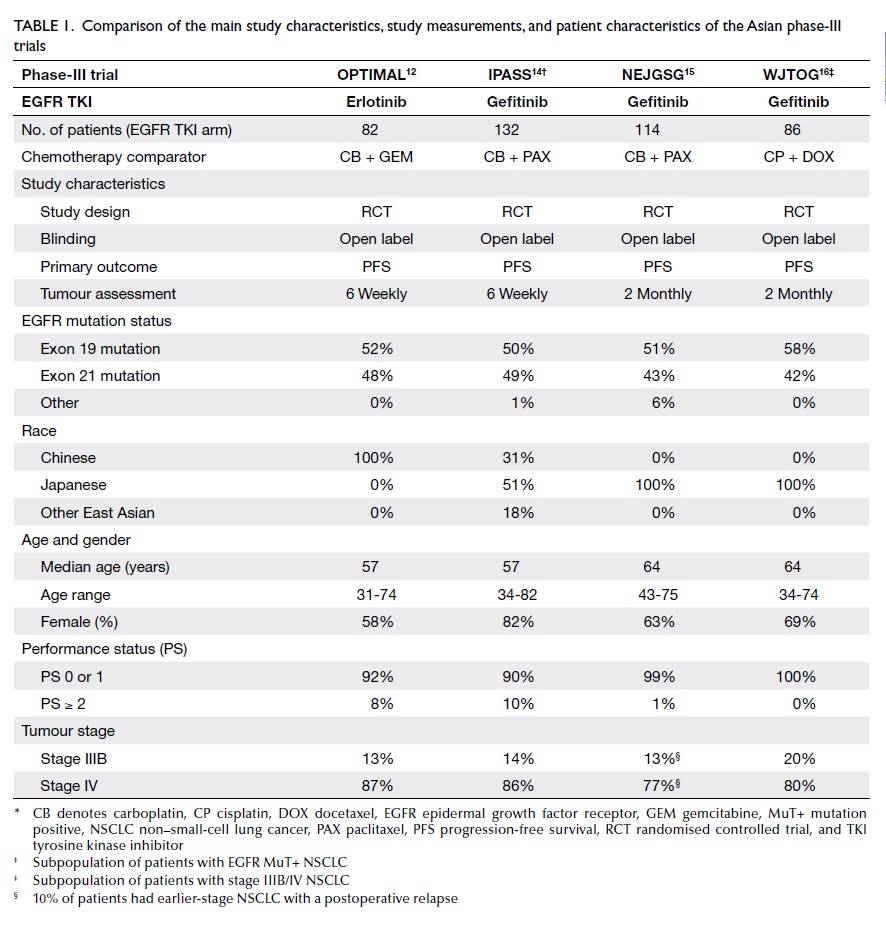
We used a fibula flap with its overlying skin
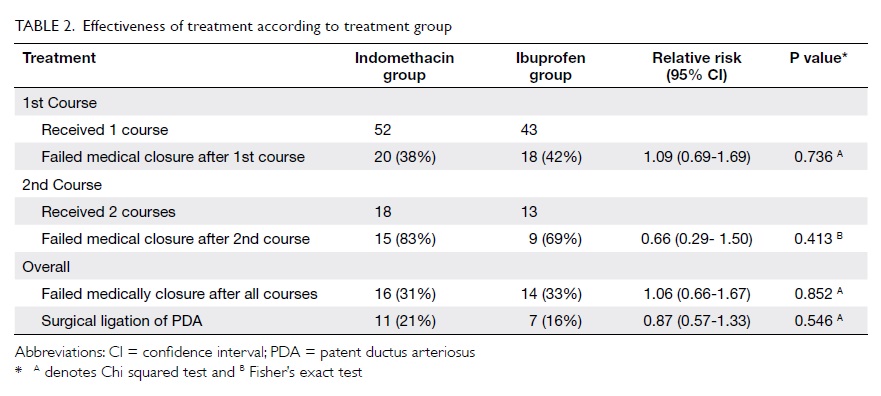
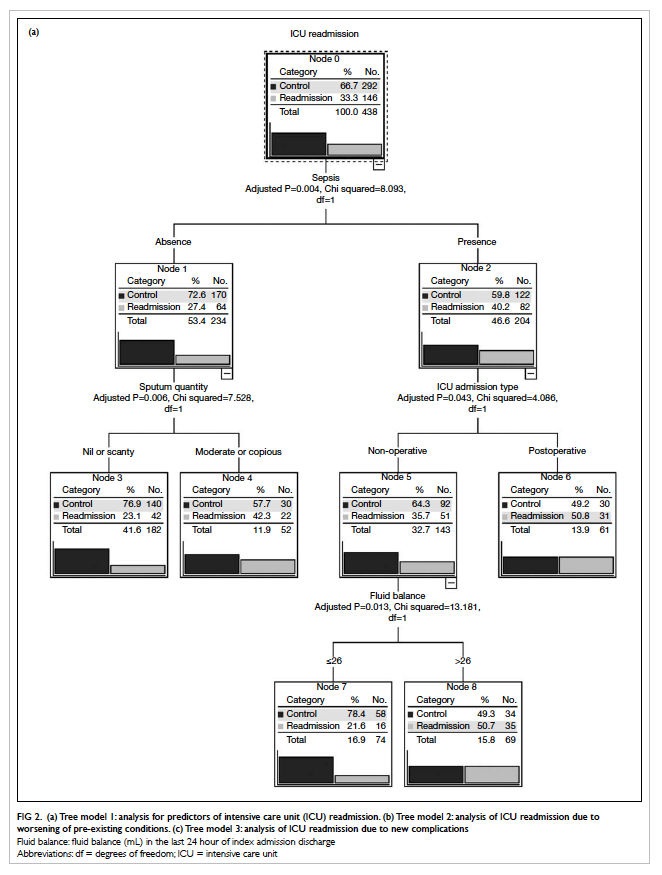
island along with a large ALT flap (Fig 2). After
anastomosis of the two sets of vessels, bleeding
from the edge of the fibula flap skin island appeared
rather sluggish. So the ALT was used for both
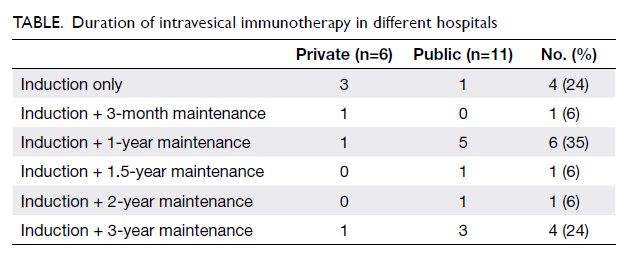
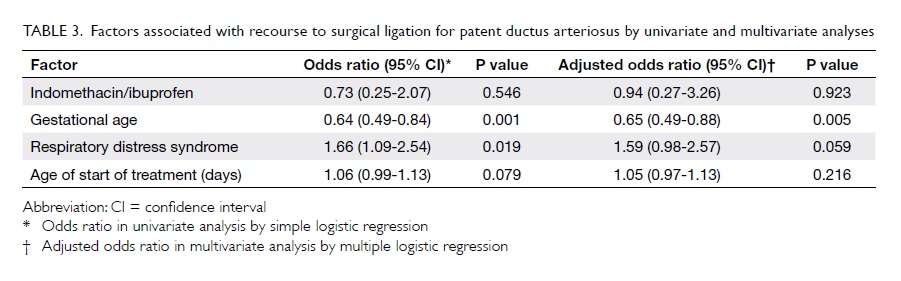
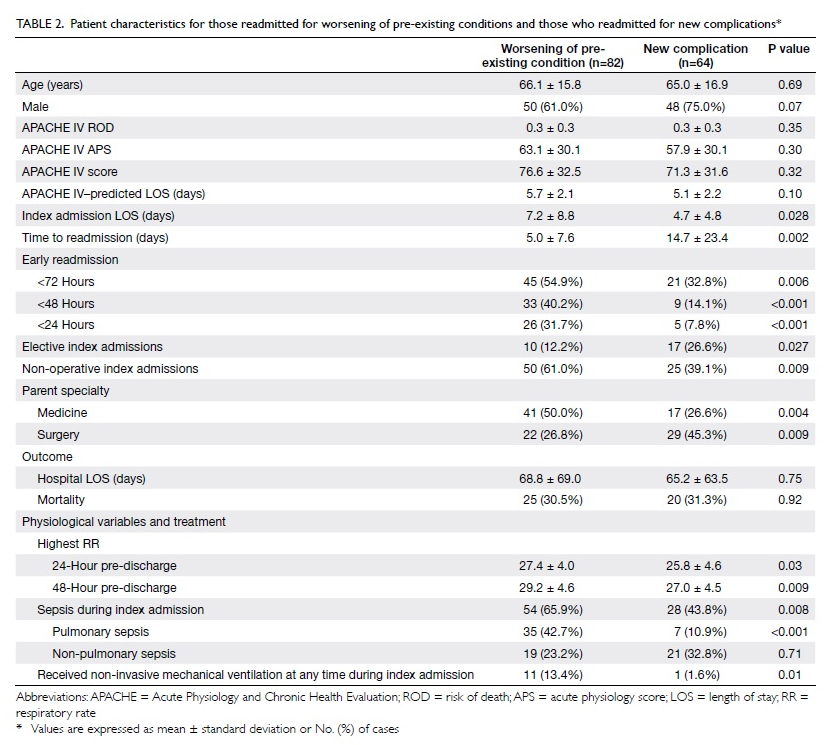
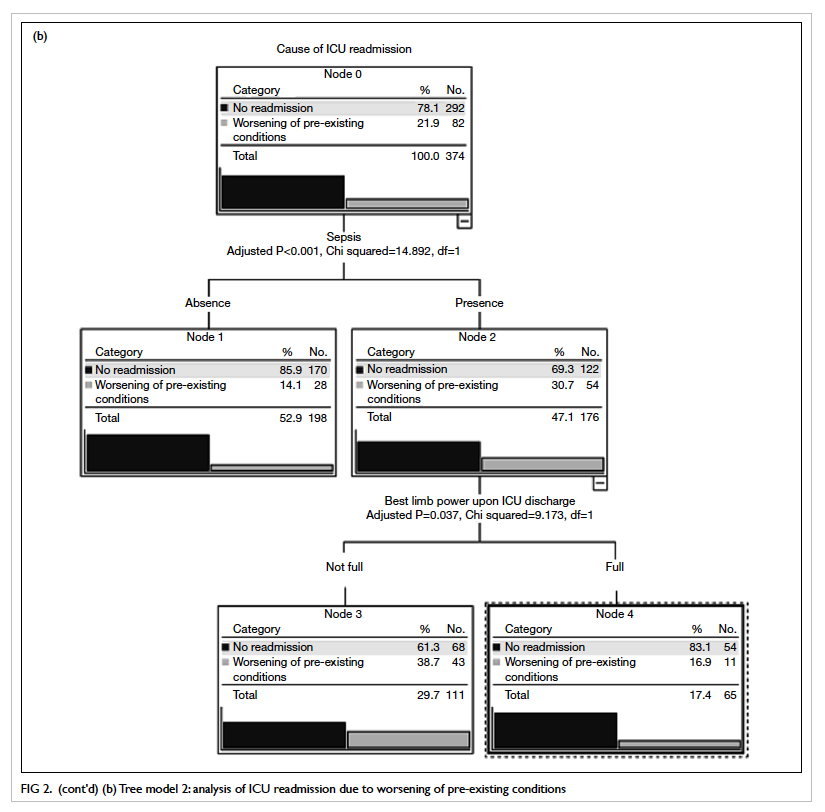
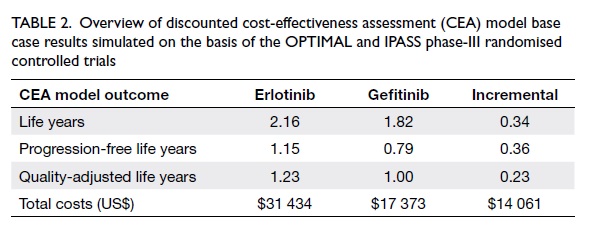
intraoral lining and external skin cover. A strip of
the ALT flap was de-epithelialised for suturing to
the lower lip remnant (Fig 3). There were no major
complications and the patient was discharged on the
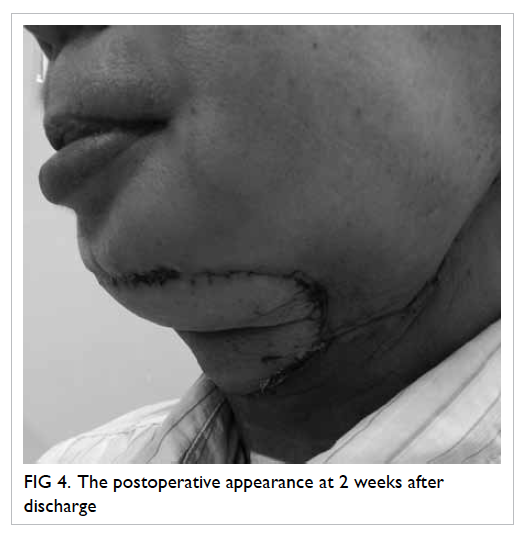
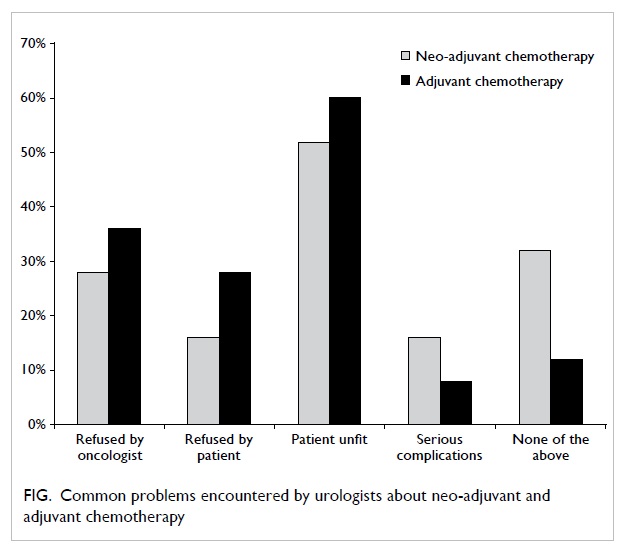
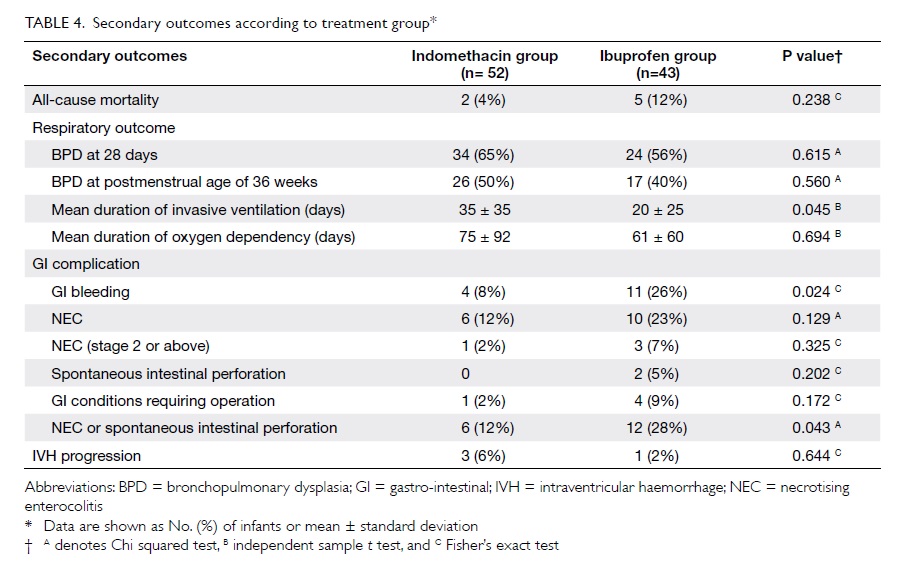
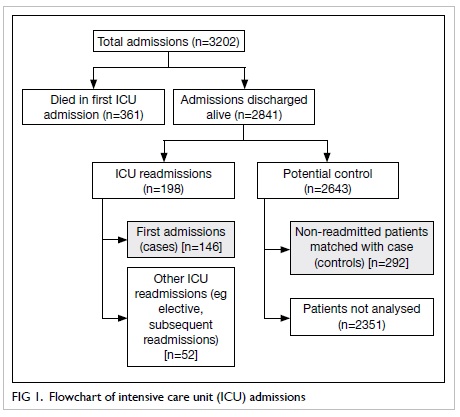
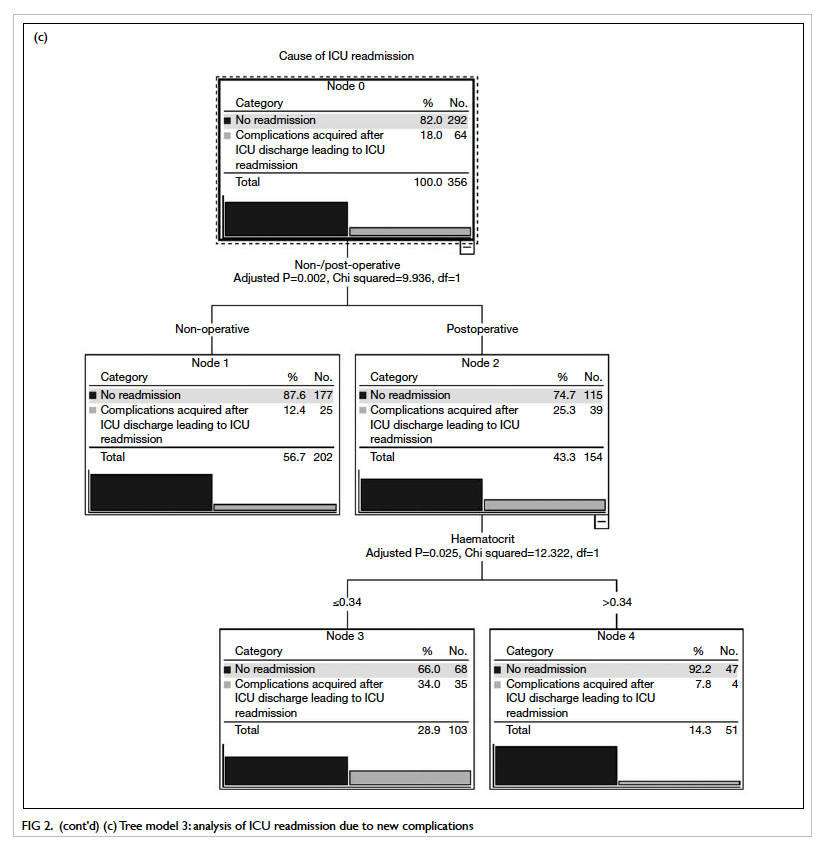
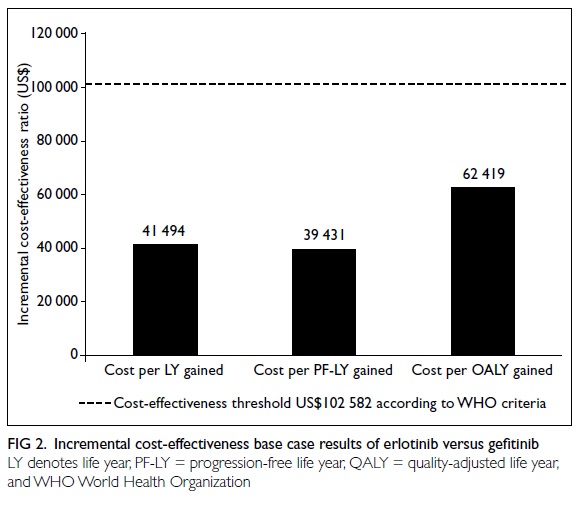
14th postoperative day. There was a good contour at
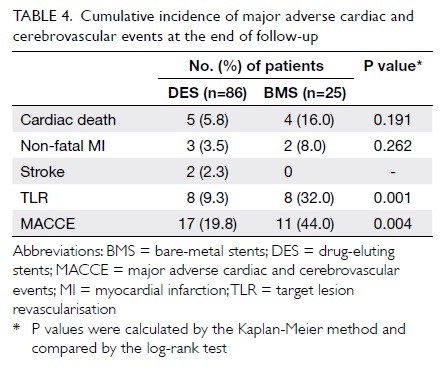
follow-up (Fig 4); the patient used a percutaneous
endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) for feeding
preoperatively but regrettably could not resume oral
feeding after this surgery and therefore remained
reliant on the PEG.
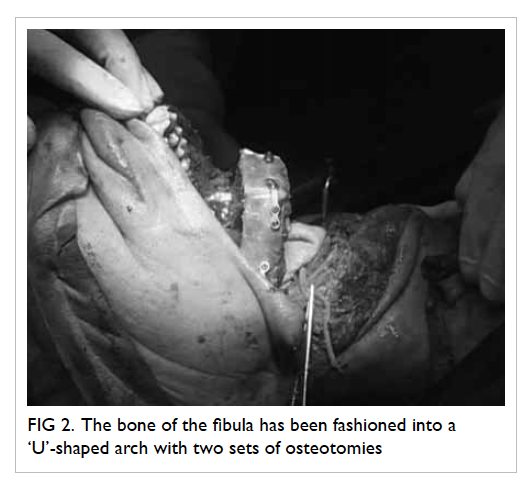
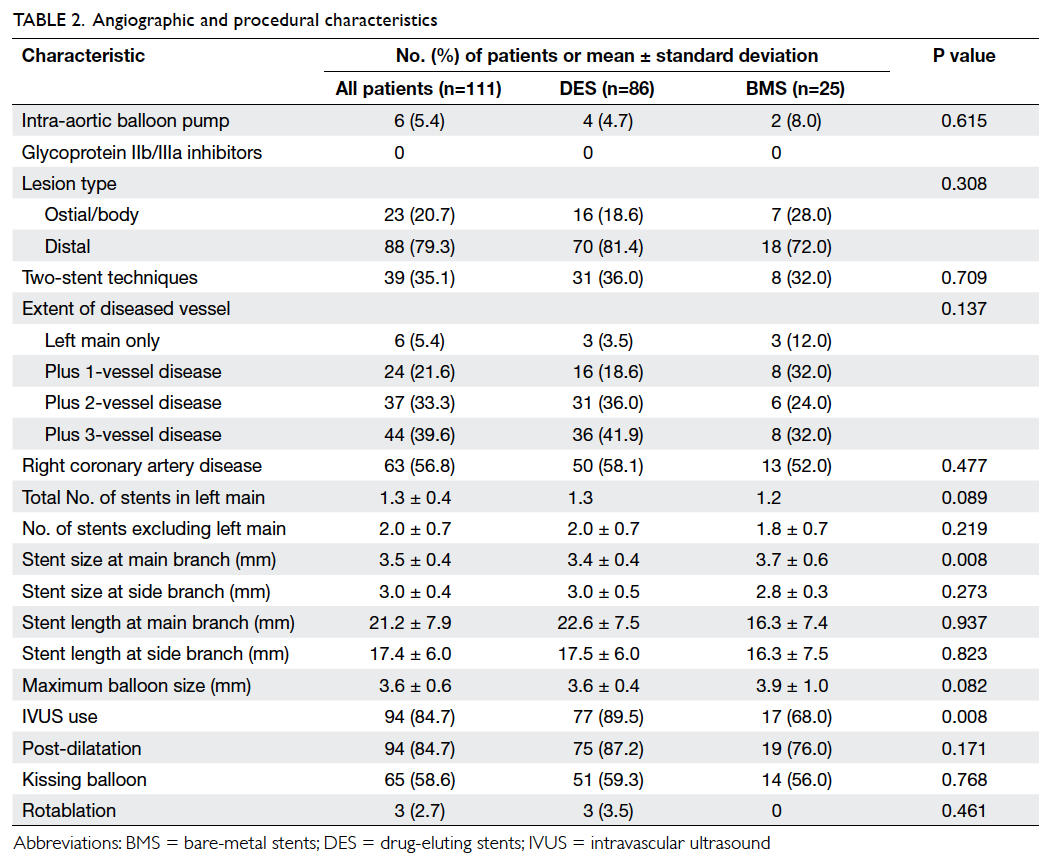
Figure 2. The bone of the fibula has been fashioned into a ‘U’-shaped arch with two sets of osteotomies
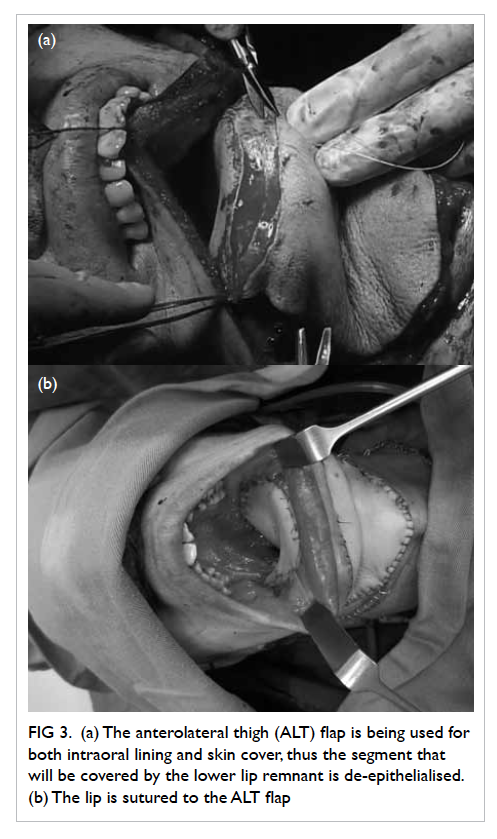
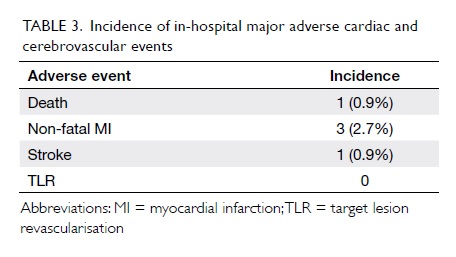
Figure 3. (a) The anterolateral thigh (ALT) flap is being used for both intraoral lining and skin cover, thus the segment that will be covered by the lower lip remnant is de-epithelialised. (b) The lip is sutured to the ALT flap
Results
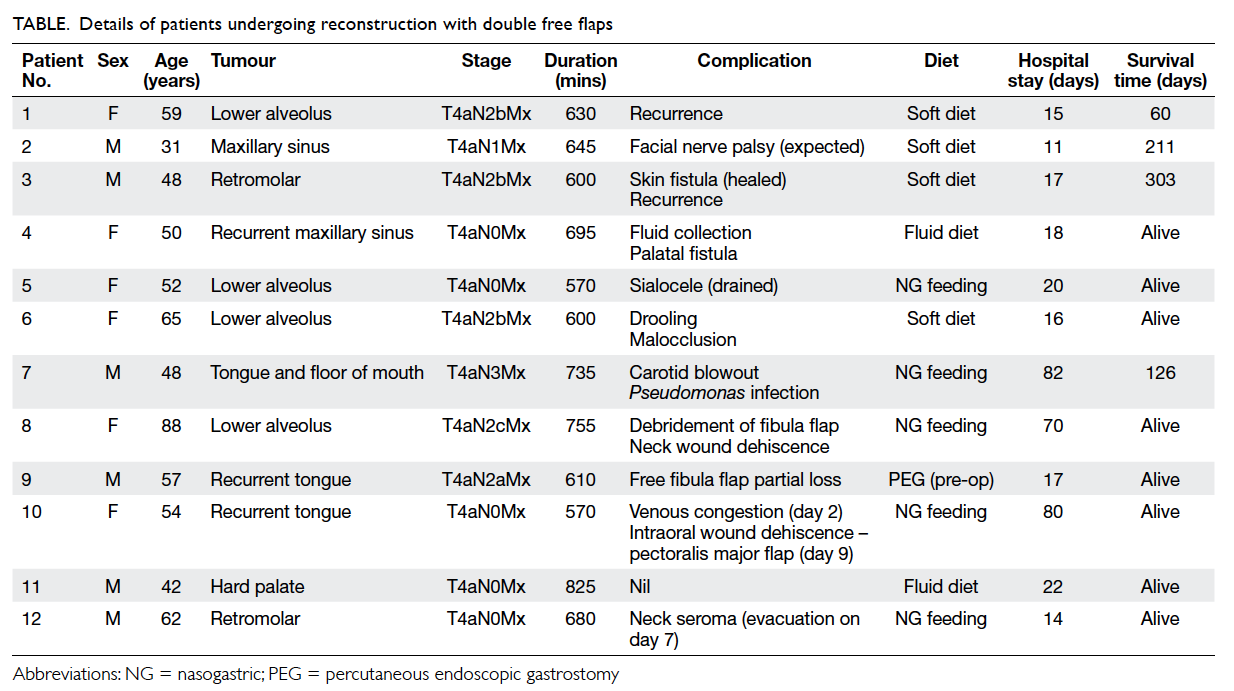
All tumours were stage T4a, with nodal status
ranging from N0-N3 (Table). During the study
period, there were six male and six female patients who had double free flap surgery. Their ages ranged
from 31 to 88 (mean, 55) years. In 10 of them, a free
fibula flap was combined with an ALT flap harvested
from the same limb; in eight of them a skin island was harvested with the bone. One patient had bilateral
ALT flaps for reconstruction of an extensive tumour
of the tongue and floor of the mouth without bone
involvement. Another patient had a free fibula flap
combined with an anteromedial thigh flap, due to
absence of suitable perforators upon dissecting the
ALT flap.
The mean total operating time was 660
minutes, which included the time for frozen section
results. Postoperative hospital stays ranged from
11 to 82 days; nine patients were discharged home
within 3 weeks. Patient 10 stayed 80 days. She
declined further surgery for an intraoral dehiscence,
which was therefore treated conservatively. Patient
7 stayed 82 days, as his recovery was complicated by
a carotid blowout on the 11th postoperative day for
which he had a surgery; subsequently a pseudomonas
wound infection was treated with antibiotics. After
surgery, seven patients were able to resume oral
feeding sufficient to maintain their body weight;
the remainder relied on tube feeding. Five patients
received adjuvant treatment (4 had chemoradiation
and 1 only had radiotherapy).
Minor postoperative complications (fluid
collections, fistulae) occurred in 67% of these patients
and usually resolved with conservative management.
More serious complications occurred in 33% of
the patients (carotid blowout, wound dehiscence/infection, and fluid collections treated surgically). In
one patient, a haematoma was treated by debridement
of the soft tissue portion of the free fibula flap that
had been de-epithelialised and ‘buried’. There were
no instances of total flap loss; two patients were
taken back to theatre for exploration and their flaps
were salvaged. One of them (patient 10) had venous
congestion of the fibula skin flap (used for intraoral lining), which was salvaged but remained swollen
and indurated. In view of a concomitant intraoral
wound dehiscence, the swollen skin island was
debrided and a pedicled ipsilateral pectoralis major
flap was harvested to close the intraoral wound.
Regrettably, although the pedicled flap survived,
the intraoral wound dehisced again, and the patient
declined to have further surgery so her wound was
managed with daily dressings (see above).
Two (17%) out of the 12 patients had
tumour recurrence during the follow-up period, and
a further two (17%) had distant metastases. Survival
from the time of surgery ranged from 60 to 303 days.
The patient survival rate at 6 months was 91%, and
at 1 year was 64%. At the time of writing this paper,
only seven of the 12 patients had been followed
up for at least 2 years, three (43%) of whom were still
alive.
Discussion
Following resection of advanced oral cancers, it is
our standard practice to use double free flaps when
needed for reconstruction of complex oromandibular
defects, particularly those involving large defects of
both bone and soft tissue. In most cases, the indication
for double free flaps was the requirement for bone
and soft tissue/skin not provided by the skin island
of a FO flap. This practice is by
no means universal; some surgeons are reluctant to
contemplate a second free flap due to the perceived increase in technical complexity, operating time,
and risk of complications. Alternative strategies
include substitution of the fibular flap with a metal
reconstruction plate, combined with a soft tissue flap
for resurfacing7; combining a fibular free flap with
pedicled regional flaps, such as the deltopectoral
flap, PMMF,8 or latissimus dorsi myocutaneous flap.
Some centres regard such cases as ‘inoperable’ and
offer palliative treatment only.
However, these simpler alternatives have
their drawbacks. The problems associated with an
alloplastic plate with a soft tissue flap for composite
mandible reconstruction are well documented,9 10 11
there being high rates of delayed plate exposure and
recourse to salvage procedures.12 In the long term,
use of vascularised bone (particularly in the FO flap)
is more successful for mandible reconstruction,2 and
was our first choice in all cases, with the possible
exception of patients with a short life expectancy (<6 months). Recourse to a regional pedicled soft tissue
flap instead of a free flap is based on its perceived
advantage in being technically easier to harvest and
involving shorter operating times.9 13 There is also
a perceived lower risk of complications through
avoiding a second set of microanastomoses. The
PMMF is the most commonly used regional flap,14
but the vascularity of its skin paddle (like that of other
regional flaps used in head and neck reconstruction)
tends to be suboptimal; if the muscle is too short,
more of the skin paddle results in a ‘random-pattern’.
Crucially, the skin islands tend to be positioned at the most distal portions and thus have the poorest
vascularity in the most critical parts.15 Chen et al16
recommends avoiding PMMFs to line the oral cavity due to a high rate of bone exposure from dehiscence.
On the contrary, surgeons such as Bianchi
et al17 have actually demonstrated better outcomes
with double free flaps compared to a combination
of one free flap with one pedicled flap. The bulk of
the muscle pedicle in regional flaps can interfere
with the inset and vascularity of a concomitant free
flap,13 and the tendency for muscle atrophy and
gravitational effects can adversely affect the final
results of reconstruction. Chen et al16 demonstrated
a lower failure rate with two free flaps (2.8%) compared
with the combination of one free and one pedicled
flap (9%). They speculated that
the bulky PMMF pedicle may actually compress the
free flap pedicle, citing the 14% to 33% frequency of
internal jugular vein thrombosis after radical neck
dissection covered with pedicled flaps.18 19 The skin
island of a regional flap also tends to be thicker,
less pliable, and thus may interfere with intraoral
function. Regional flaps may be limited in other ways
(eg lack of necessary tissue components or specific
tissue volume), which compromise the final aesthetic
and functional outcomes.20
Although on average, a single free flap can take
1.5 hours longer than a PMMF to harvest, Tsue et
al21 found that the operating time for double flaps
can be 3 hours shorter than for a one free and one
pedicled combination. They explained this by citing
possible bias by surgeons choosing to use a second
pedicled flap, when the resection time was longer,
and surgeons working faster whenever two free
flaps were anticipated. Guillemaud et al22 found
no significant difference in the duration of surgery
and complication rate when comparing double free
and one free and one pedicled surgeries. In the end,
the duration of surgery should not be a factor in
determining the type of reconstruction.23
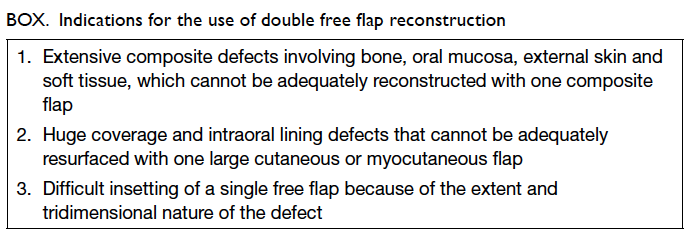
Proposed indications for the use of double
free flaps are listed in the Box.20 The reconstruction
of defects resulting from tumour resection in the
head and neck region is a challenge, particularly
when a composite of tissues is required or the defect
is too large to cover by a single flap. Recourse to
two free flaps allows more versatility and flexibility
when reconstructing such complex defects. The
best osseous and soft tissue elements may be
independently selected, yielding appropriate tissue
characteristics for ideal defect reconstruction.
Using two separate thin pliable free flaps rather than
bulky pedicled flaps may allow easier insetting and
better restoration of the 3-dimensional anatomical
boundaries,24 and thus both the functional and
aesthetic outcomes can be addressed. With free
flaps, there is also the potential for including other
components such as nerves for sensate flaps.24
Good-quality soft tissue coverage is needed
to reduce the risk of plate exposure12; even when
the skin component of the FO
flap can provide adequate surface cover, there
is usually an overall shortage of soft tissue. Soft
tissue reconstruction is as important as bone
reconstruction25 in determining a satisfactory
outcome, as deficiency of the latter tissues is
poorly tolerated in the head and neck,26 and may
lead to inadequate obliteration of dead spaces (eg
from resection of masticators, buccal fat pad, and
parotid). This causes accumulation of fluid which
may become secondarily infected,16 and threaten
micro-anastomoses and lead to contractures, and
poor cosmetic outcomes or functionality that can
lead to trismus, as well as contraction of the floor
of the mouth with tethering of the tongue with
difficulties in swallowing and speech.27 Therefore,
even in the absence of bone loss, a double free flap
reconstruction can be advantageous especially if
soft tissue loss is substantial or beyond the reach of
pedicled alternatives.
The use of two simultaneous free flaps
undoubtedly poses technical difficulties, by
increasing potential patient morbidity and is time-consuming.
Although it is not our intention to
promote double free flap reconstruction as a ‘routine’
reconstruction procedure, we wish to highlight it as
an option, at least for tumours that are often deemed
‘inoperable’. Balasubramanian et al28 demonstrated
that advanced ‘inoperable’ tumours such as T4b (in 7
of 21 cases) can be safely operated on; having double free
flap reconstruction in the armamentarium allows
surgeons to be more aggressive with extirpation.
With careful patient selection, the duration of
surgery, hospital stays, and complications need
not be prohibitive compared to single free flap
operations.25 Wei et al20 suggest that double free
flaps should be restricted to patients with primary
cancers, avoiding their use in those with recurrent
cancers or second primaries. Nevertheless, in our
series three patients presented with recurrent
cancer. Individual patients should be assessed on a
case-by-case basis—a PMMF could be considered
to cover the skin of the neck, whilst reconstruction
plates may be used to reconstruct short posterior or
lateral mandible defects, particularly in those with a short life expectancy.
Our study shows that double free flap
reconstruction can be worthwhile in patients with
T4 tumours with a flap survival rate of 100% and
a patient survival rate of 64% at the time of going
to press. Just over half of our patients were able to
resume oral feeding, which is somewhat lower than
that in some other studies,28 29 and may be related
to the locally advanced extent of their tumours,
particularly with regard to tongue involvement.
References
1. Hidalgo DA, Rekow A. A review of 60 consecutive fibula free flap mandible reconstructions. Plast Reconstr Surg 1995;96:585-96. CrossRef
2. Tan BK, Wong CH. An anomalous septocutaneous perforator to the skin paddle of the fibula osteocutaneous flap originating from the posterior tibial artery. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2009;62:690-2. CrossRef
3. Chiu T, Wong EW, Burd A, Vlantis A. Perforator transfer in the antero-lateral thigh flap. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2013;66:1012-3. CrossRef
4. Lin PY, Kuo YR, Chien CY, Jeng SF. Reconstruction of head and neck cancer with double flaps: comparison of single and double recipient vessels. J Reconstr Microsurg 2009;25:191-5. CrossRef
5. Wei FC, Demirkan F, Chen HC, Chen IH. Double free flaps in reconstruction of extensive composite mandibular defects in head and neck cancer. Plast Reconstr Surg 1999;103:39-47. CrossRef
6. Wei FC, Celik N, Chen HC, Cheng MH, Huang WC. Combined anterolateral thigh flap and vascularized fibula osteoseptocutaneous flap in reconstruction of extensive composite mandibular defects. Plast Reconstr Surg 2002;109:45-52. CrossRef
7. Boyd JB, Mulholland RS, Davidson J, et al. The free flap and plate in oromandibular reconstruction: long-term review and indications. Plast Reconstr Surg 1995;95:1018-28. CrossRef
8. Ariyan S. The pectoralis major myocutaneous flap. A versatile flap for reconstruction in the head and neck. Plast Reconstr Surg 1979;63:73-81. CrossRef
9. Blackwell KE, Buchbinder D, Urken ML. Lateral mandibular reconstruction using soft-tissue free flap and plates. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1996;122:672-8. CrossRef
10. Cohen M, Schultz RC. Mandibular reconstruction. Clin Plast Surg 1985;12:411-22.
11. Shpitzer T, Gullane PJ, Neligan PC, et al. The free vascularized flap and the flap plate option: comparative results of reconstruction of lateral mandibular defects. Laryngoscope 2000;110:2056-60. CrossRef
12. Wei FC, Celik N, Yang WG, Chen IH, Chang YM, Chen HC. Complications after reconstruction plate and soft-tissue free flap in composite mandibular defects and secondary salvage reconstruction with osteocutaneous flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 2003;112:37-42. CrossRef
13. Blackwell KE, Buchbinder D, Biller HF, Urken ML. Reconstruction of massive defects in the head and neck: the role of simultaneous distant and regional flaps. Head Neck 1997;19:620-8. CrossRef
14. Lerrick AJ, Zak MJ. Oral cavity reconstruction with simultaneous free and pedicled composite flaps. Operat Tech Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2000;11:76-89. CrossRef
15. Shah JP, Haribhakti V, Loree TR, Sutaria P. Complications of the pectoralis major myocutaneous flap in head and neck reconstruction. Am J Surg 1990;160:352-5. CrossRef
16. Chen HC, Demirkan F, Wei FC, Cheng SL, Cheng MH, Chen IH. Free fibula osteoseptocutaneous-pedicled pectoralis major myocutaneous flap combination in reconstruction of extensive composite mandibular defects. Plast Reconstr Surg 1999;103:835-45. CrossRef
17. Bianchi B, Ferri A, Ferrari S, et al. Reconstruction of lateral through and through oro-mandibular defects following oncological resections. Microsurgery 2010;30:517-25. CrossRef
18. Fisher CB, Mattox DE, Zinreich JS. Patency of the internal jugular vein after functional neck dissection. Laryngoscope 1988;98:923-7. CrossRef
19. Brown DH, Mulholland S, Yoo JH, et al. Internal jugular vein thrombosis following modified neck dissection: implications for head and neck flap reconstruction. Head Neck 1998;20:169-74. CrossRef
20. Wei FC, Yazar S, Lin CH, Cheng MH, Tsao CK, Chiang YC. Double free flaps in head and neck reconstruction. Clin Plastic Surg 2005;32:303-8. CrossRef
21. Tsue TT, Desyatnikova SS, Deleyiannis FW, et al. Comparison of cost and function in reconstruction of the posterior oral cavity and oropharynx. Free vs pedicled soft tissue transfer. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1997;123:731-7. CrossRef
22. Guillemaud JP, Seikaly H, Cote DW, et al. Double free-flap reconstruction: indications, challenges, and prospective functional outcomes. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2009;135:406-10. CrossRef
23. Schusterman MA, Horndeski G. Analysis of the morbidity associated with immediate microvascular reconstruction in head and neck cancer patients. Head Neck 1991;13:51-5. CrossRef
24. Urken ML, Weinberg H, Vickery C, et al. The combined sensate radial forearm and iliac crest free flaps for reconstruction of significant glossectomy-mandibulectomy defects. Laryngoscope 1992;102:543-8. CrossRef
25. Urken ML, Weinberg H, Vickery C, Buchbinder D, Lawson W, Biller HF. Oromandibular reconstruction using microvascular composite free flaps. Reports of 71 cases and a new classification scheme for bony, soft-tissue, and neurologic defects. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1991;117:733-44. CrossRef
26. Andrades P, Bohannon IA, Baranano CF, Wax MK, Rosenthal E. Indications and outcomes of double free flaps in head and neck reconstruction. Microsurgery 2009;29:171-7. CrossRef
27. Urken ML, Buchbinder D, Weinberg H, et al. Functional evaluation following microvascular oromandibular reconstruction of the oral cancer patient: a comparative study of reconstructed and non-reconstructed patients. Laryngoscope 1991;101:935-50. CrossRef
28. Balasubramanian D, Thankappan K, Kuriakose MA, et al. Reconstructive indications of simultaneous double free flaps in the head and neck: a case series and literature review. Microsurgery 2012;32:423-30. CrossRef
29. Hanasono MM, Weinstock YE, Yu P. Reconstruction of extensive head and neck defects with multiple simultaneous free flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg 2008;122:1739-46. CrossRef